Maltodextrin vs. Dextrose
Maltodextrin vs. Dextrose

Maltodextrin and Dextrose are two of the most popular carbohydrate supplements that are doing the rounds in the world of bodybuilding. In this guide, we will be gaining invaluable insights on the battle of Maltodextrin vs. Dextrose for supremacy.
Maltodextrin can be defined as a polysaccharide that undergoes partial hydrolysis during processing to break down the starches into shorter chains of glucose molecules. A carbohydrate derived from starchy foods such as corn, rice, or potatoes, Maltodextrin serves as a readily available source of energy. It is composed of chains of glucose molecules of varying lengths. These chains may include shorter and longer glucose units, which contribute to its versatility in terms of digestion and absorption.
One of the biggest advantages of Maltodextrin is that it can be quickly digested by the body that results in a significant increase in blood glucose levels, providing a readily available energy source. Athletes, bodybuilders, and fitness enthusiasts prefer using Maltodextrin as a carbohydrate source for loading glycogen stores before endurance events as it is effective for pre-event energy needs. Maltodextrin is commonly included in sports drinks and intra-workout supplements to provide a quick and sustained source of energy during prolonged exercise sessions. Having a mild and neutral taste, Maltodextrin can be added to different beverages and foods without significantly altering their flavors.
On the other hand, Dextrose is a common ingredient in post-workout supplements or shakes to kick start the recovery process. Its quick absorption helps replenish glycogen stores and promote muscle recovery after intense exercise. This most basic form of carbohydrate is naturally present in various foods, including fruits and honey, but it can also be commercially produced from cornstarch.
A monosaccharide, Dextrose has a simple structure that allows for rapid absorption and utilization by the body. Dextrose has the unique ability of stimulating the release of insulin in the body that plays an important role in nutrient uptake by muscle cells. This response of insulin is usually leveraged to maximize nutrient delivery during the post-workout window.
The primary difference between Maltodextrin and Dextrose is that Maltodextrin has a more intricate structure and is a complex carbohydrate. On the other hand, Dextrose has a straightforward structure and is a monosaccharide consisting of a single glucose molecule. Dextrose doesn't require digestion and can be quickly absorbed as-is into the bloodstream while Maltodextrin requires partial hydrolysis during digestion to break down its glucose chains into individual glucose molecules for absorption.
Also, Maltodextrin has a higher glycemic index compared to complex carbohydrates but lower than that of Dextrose. Furthermore, the use of Maltodextrin can cause an enhancement in the levels of blood glucose but still its impact is lower on the release of insulin compared to Dextrose.
Maltodextrin is an excellent choice for athletes, bodybuilders, and fitness enthusiasts who regularly engage themselves in longer-duration exercises or as part of a pre-event carbohydrate-loading strategy. On the other hand, Dextrose is an ideal choice for rapid energy replenishment like post-workout recovery when there is an almost immediate requirement for glycogen replenishment and a spike in the levels of insulin is required to support nutrient intake.
Maltodextrin is a better choice for individuals who are sensitive to insulin or those looking for a carbohydrate source with a milder impact on insulin levels. On the other hand, Dextrose can be a better choice for those who are intentionally seeking a more pronounced insulin response, such as individuals aiming to maximize nutrient delivery to muscles after intense workouts.
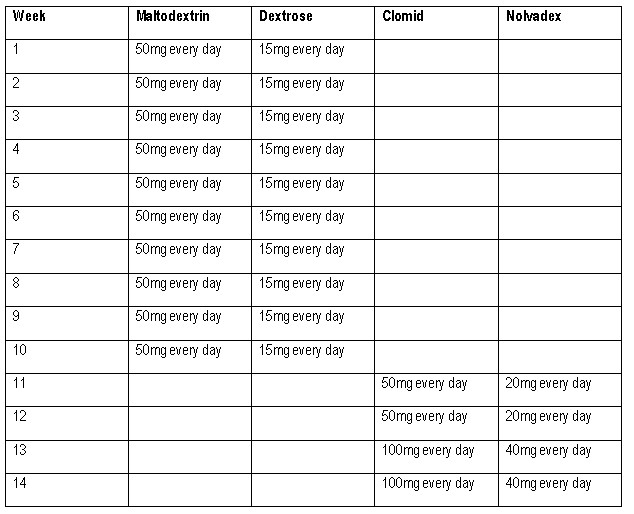
The recommended dose of Maltodextrin for men is 50-100mg every day in cycles of 10-18 weeks. For women, the recommended dose of Maltodextrin is 20-40mg every day in cycles of 6-10 weeks. The recommended dose of Dextrose for men is 10-25gm every day in cycles of 10-18 weeks. For women, the recommended dose of Dextrose is 5-10gm every day in cycles of 6-10 weeks.
Cycles For Men
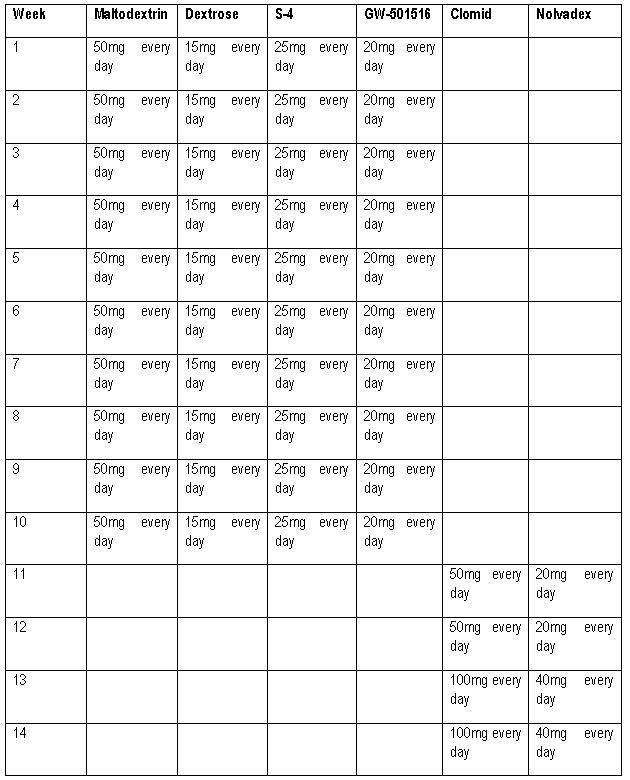
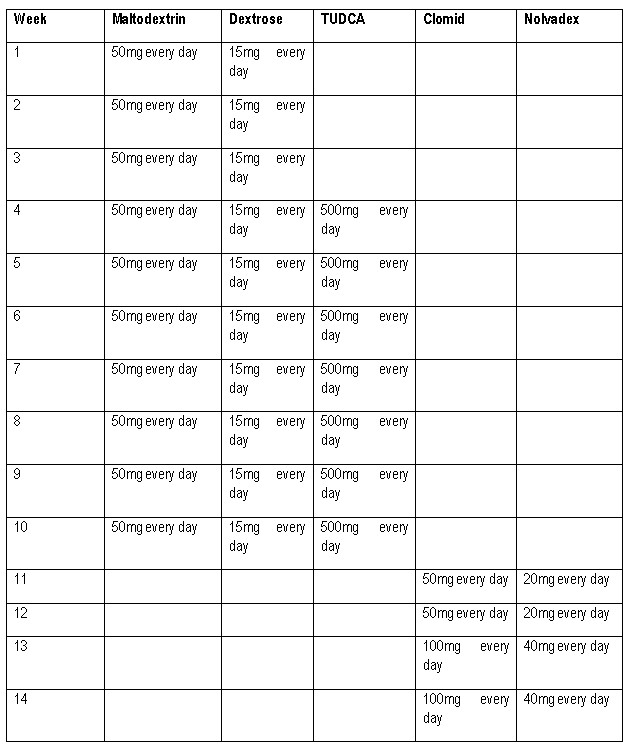
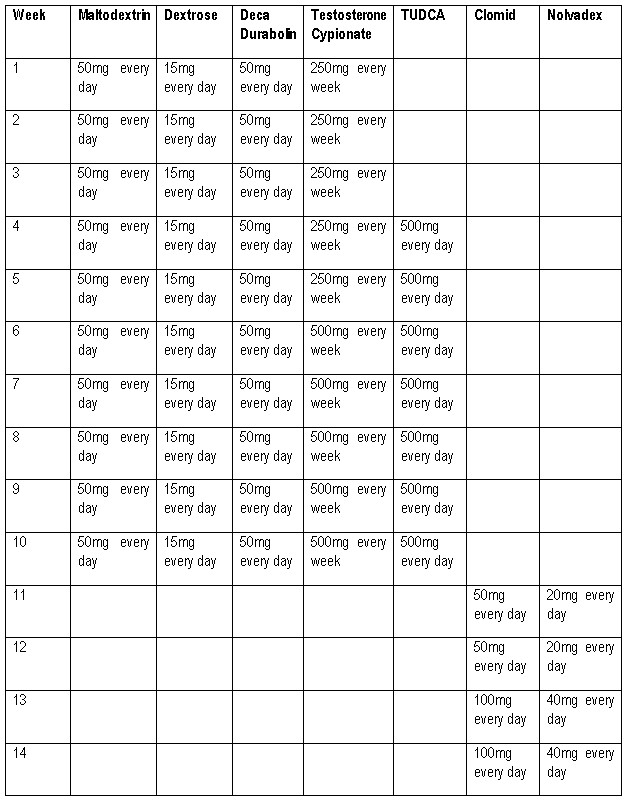
Cycles For Women
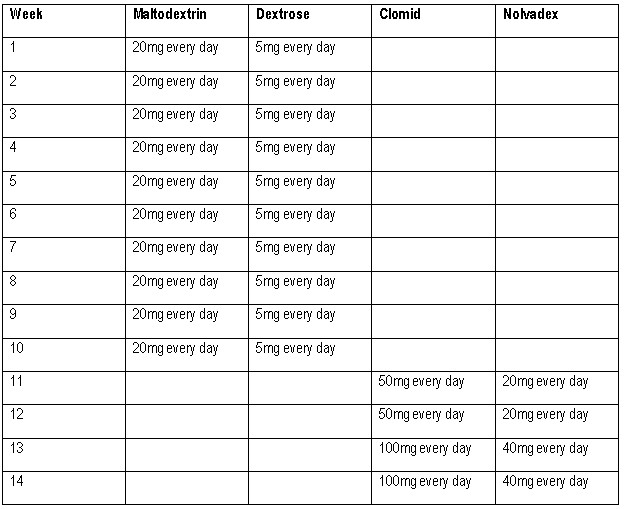
We hope that this guide on the battle of Maltodextrin vs. Dextrose was useful to you.
Recommended product - Pro Nutrition LGD-4033